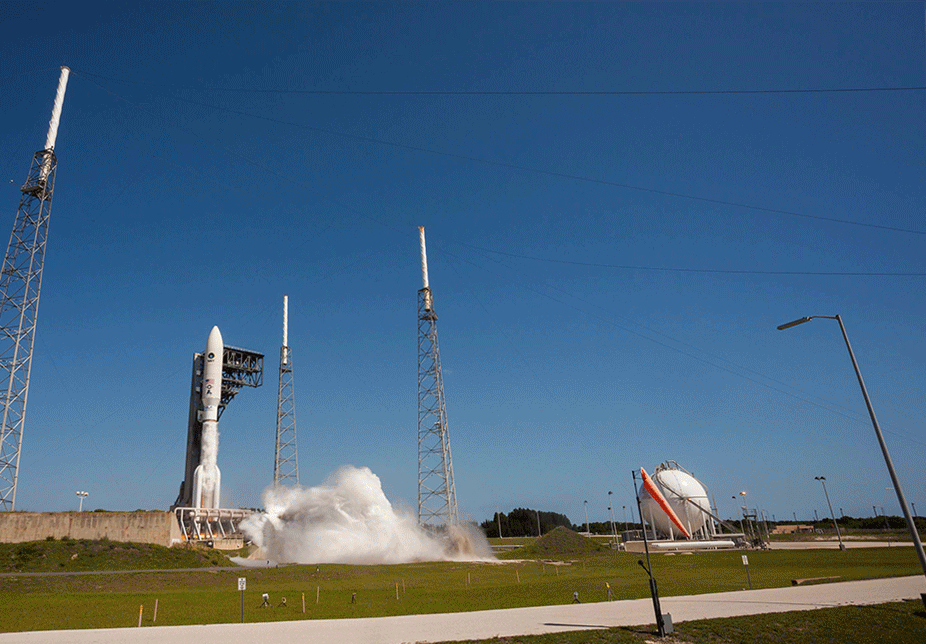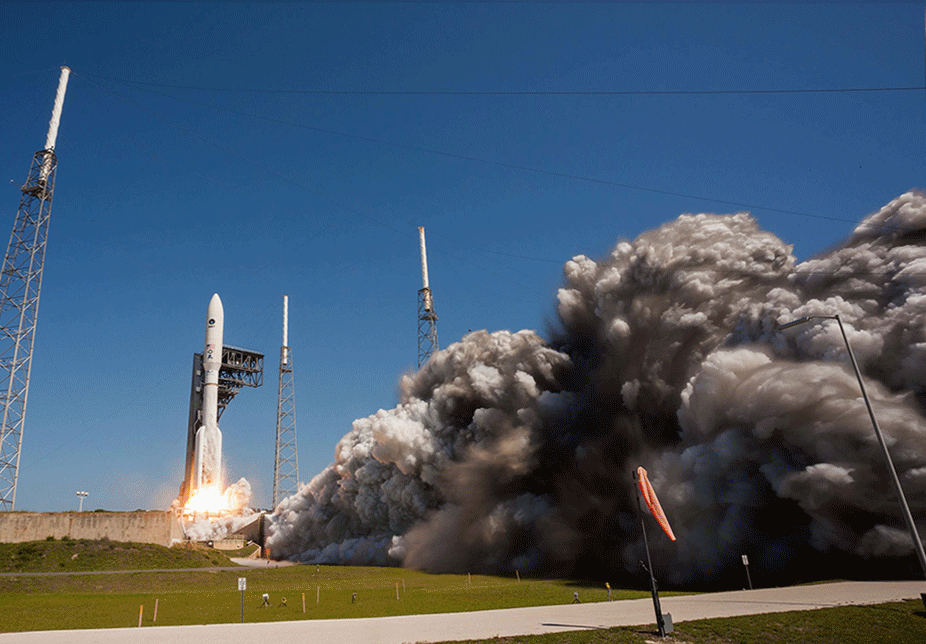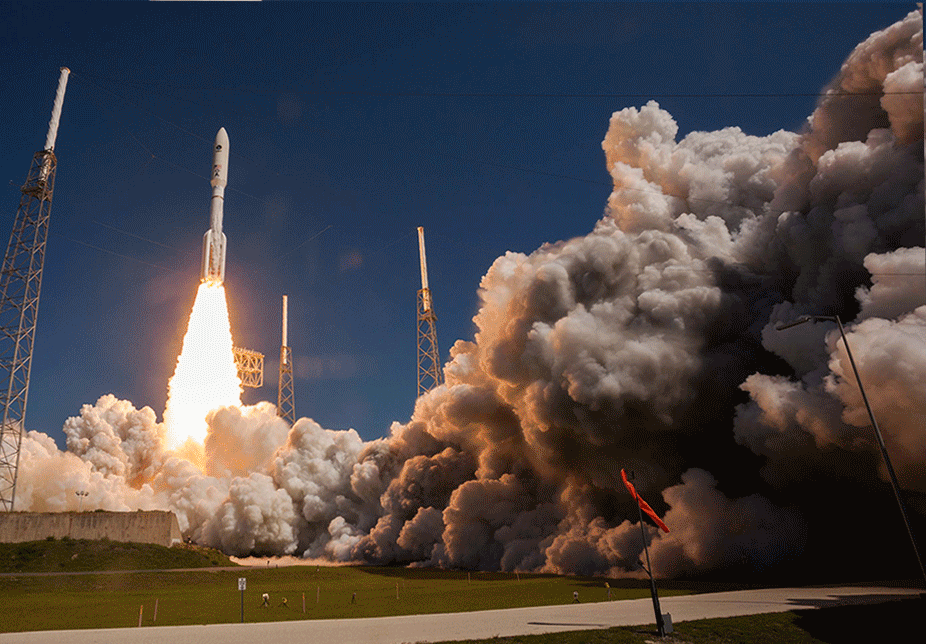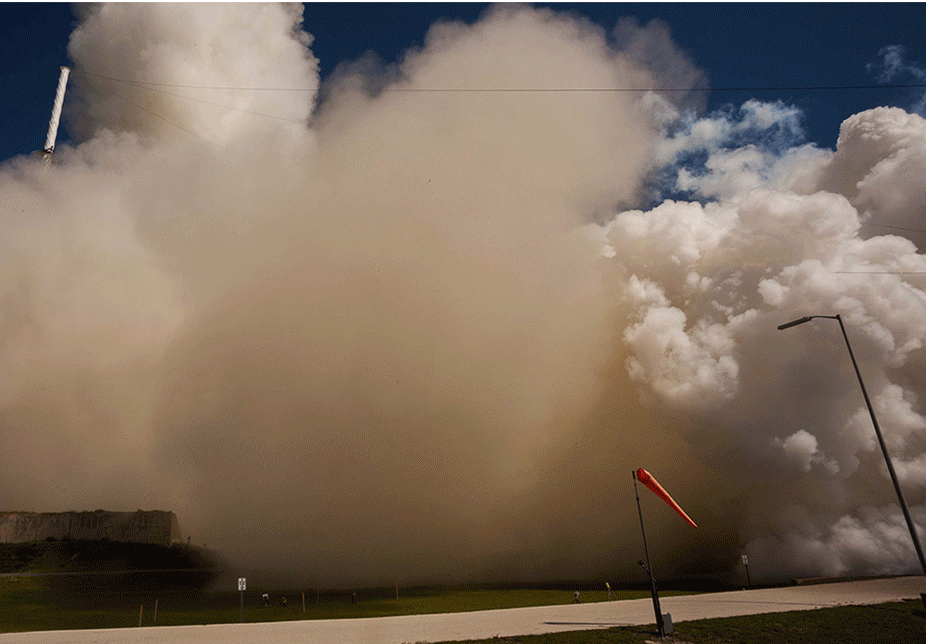
 U.S. Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM) at Offutt Air Force Base, Neb., has approved the U.S. Navy’s next-generation narrowband satellite communication (SATCOM) system for expanded operational use, paving the way for Navy and Marine Corps early-adopter commands to use the system on deployment as early as this fall, primarily in the Pacific theater.
U.S. Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM) at Offutt Air Force Base, Neb., has approved the U.S. Navy’s next-generation narrowband satellite communication (SATCOM) system for expanded operational use, paving the way for Navy and Marine Corps early-adopter commands to use the system on deployment as early as this fall, primarily in the Pacific theater. 
Mobile User Objective System (MUOS), the Navy’s on-orbit, five-satellite constellation, began providing legacy satellite communications shortly after the first MUOS satellite launch in 2012.
Each MUOS satellite has dual-capability, explains Steve Davis at Space and Naval Warfare Systems Command. The legacy satellite communications payload was designed to maintain legacy narrowband communications for the Department of Defense (DoD) while the advanced MUOS capability came on line.
The full-suite MUOS payload, known as Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) waveform, adapts commercial cellular technology to enable warfighters to communicate beyond-line-of-sight (BLOS) more securely and reliably than ever before, and with 10 times the capacity compared to the legacy capability.
Operators today with MUOS WCDMA radios are connecting beyond line-of-sight around the globe, transmitting simultaneous voice, video and mission data on an Internet Protocol-based system that connects to military networks, Davis adds.
“Narrowband communication is used by every combatant command, aboard ships at sea and multiple aircraft platforms, and by ground troops in a variety of warfighting applications, such as special operations,” says Rear Adm. Carl Chebi, who leads the Navy’s Program Executive Office (PEO) for Command, Control, Communications, Computers, and Intelligence (C4I) and PEO Space Systems.
The system is expected to be declared fully operational following multi-service test and evaluation in summer 2019. The Marine Corps is slated to begin initial MUOS fielding in the fourth quarter of 2018, followed by initial operational capability in the first quarter of 2019.

Learn more
-
Bookmark http://www.sae.org/news to keep pace with the latest aerospace technology news & information.
-
Read SAE International content on satellite communications
-
Learn about AeroPaks, a cost-effective and convenient way to access the 8,000+ SAE aerospace standards, specifications, recommended practices, and resource documents available in SAE MOBILUS. In addition, AeroPak customers can search and download any of the nearly 15,000 historical versions of SAE’s Aerospace Standards and Aerospace Material Specifications.
-
Subscribe to SAE MOBILUS for access to more than 200,000 resources covering a wide range of technologies all surrounding the aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicle industries. These content types include: aerospace standards, ground vehicle standard, historical standards, technical papers, eBooks, magazines, and video.
Courtney E. Howard is editorial director and content strategist at SAE International, Aerospace Products Group. Contact her by e-mail at courtney.howard@sae.org.
Continue reading »